Since its introduction in the late 19th century, plastic injection molding has become a manufacturing staple and revolutionized plastic production. Since the 19th century, the technology has grown and evolved and even today, injection molds fall into two primary categories: hot runner and cold runner systems. Each type boasts its pros and cons which makes them best for specific products and applications. Knowing the difference between these two systems allows you to have a more informed conversation with your plastic injection molding supplier to determine the best option for your application.
Cold Runner Mold
A cold runner mold consists of two-to-three plates held in the mold base. The material is injected into the mold via a nozzle sprue, which fills a network of runners leading to the cavities. The reason this system is called a cold runner mold is that the runners are unheated and utilized as a delivery system to distribute molten plastic into the mold cavities.
Advantages
There are multiple advantages to utilizing a cold runner mold including:
- It can handle multiple commodities and types of thermoplastics.
- It can implement quicker design changes.
- Greater flexibility than the hot runner system.
- Lower maintenance cost.
- More cost-effective than the hot runner system.
Disadvantages
While there are many advantages to this type of plastic injection molding system, there are also a few disadvantages such as:
- Manual separation of the runner from the finished part post-run.
- Runners must be reground and recycled to avoid material waste post-run.
- Slower cycle speeds than with hot runner systems.
Hot Runner Mold
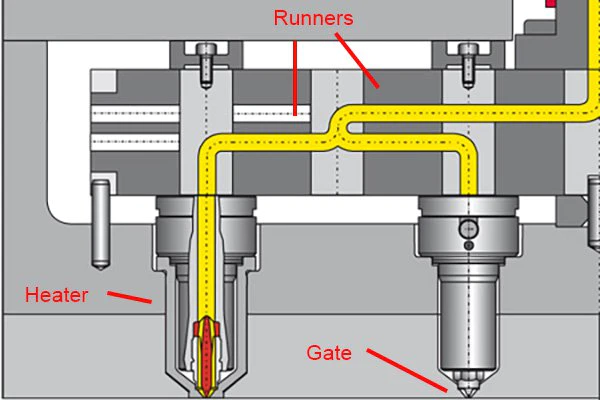
A hot runner mold is comprised of two heated plates within the manifold system. The manifold aids in maintaining a consistent temperature across the runners, which aligns with the heating cylinder. Heated runners transport and deliver molten plastic to nozzles that fill the core to create the final part. This plastic injection molding system is encased in a separate plate which remains stationary throughout the cycle. The core plate opens with the final part without the runners attached.
Advantages
A hot runner mold offers numerous advantages such as:
- Eradicates robotics to remove the runners.
- Faster production time than a colder runner system.
- Increase in the overall efficiency of the molding automation process.
- Potential waste reduction during the molding process.
- Runner elimination reduces the overall cost due since there are fewer post-production activities.
Disadvantages
There are a few disadvantages to utilizing a hot runner system including:
- Additional heating sources are required, which adds to the cost.
- More tooling expense than a cold runner system.
- Overall higher cost of implementation than cold runner systems.
In summary, cold runner molds are an excellent option for fast design changes, offering excellent flexibility but have a slower output which increases the unit cost. On the other hand, hot runner molds are more efficient than cold runner molds but also require higher tooling and upfront costs. The decision to select one of the other is based on the need of each client, their budget, and what is being manufactured.